Serving Size and Dietary Considerations: Nutrition Facts Of Grilled Cheese
Nutrition facts of grilled cheese – Understanding the nutritional content of a grilled cheese sandwich and adapting it to various dietary needs is crucial for incorporating it into a balanced diet. The nutritional values can vary significantly based on the type and amount of bread, cheese, and added ingredients. This section provides a clearer picture of these variations and offers suggestions for modifications.
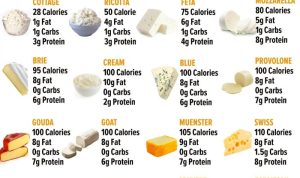
Nutritional information for a grilled cheese sandwich is highly dependent on the specific ingredients used. The following table provides estimates based on common ingredients. Remember that these are approximations, and actual values may vary.
Nutritional Information for Different Serving Sizes
| Serving Size | Calories | Fat (g) | Protein (g) | Carbohydrates (g) | Fiber (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Half Sandwich (1 slice bread, 1/2 cheese) | 150-200 | 8-12 | 7-10 | 15-20 | 1-2 |
| Whole Sandwich (2 slices bread, 1 cheese slice) | 300-400 | 16-24 | 14-20 | 30-40 | 2-4 |
| Two Sandwiches (4 slices bread, 2 cheese slices) | 600-800 | 32-48 | 28-40 | 60-80 | 4-8 |
Note: These values are estimates and can vary depending on the type of bread and cheese used, as well as the amount of butter or oil used in cooking.
Dietary Adaptations for Grilled Cheese Sandwiches, Nutrition facts of grilled cheese
Adapting the classic grilled cheese to accommodate various dietary needs is relatively straightforward. Simple ingredient substitutions can make this comfort food accessible to a wider range of individuals.
- Vegetarian: Use vegetarian cheese alternatives (many are available in supermarkets) to maintain the classic flavor profile.
- Vegan: Replace cheese with vegan cheese alternatives (many brands offer convincing alternatives) and use vegan butter or oil for cooking.
- Low-Fat: Opt for lower-fat bread and cheese varieties. Reduce the amount of butter or oil used for cooking, or use a cooking spray instead.
- Low-Sodium: Choose low-sodium bread and cheese options. Avoid adding extra salt during preparation.
Health Benefits and Drawbacks of Grilled Cheese
A grilled cheese sandwich, while undeniably delicious, should be considered within the context of a balanced diet. While it provides carbohydrates for energy and protein from the cheese, it is relatively high in saturated fat and sodium, depending on the ingredients. Excessive consumption can contribute to weight gain and increased risk of heart disease. However, a grilled cheese sandwich made with whole-wheat bread and lower-fat cheese can offer a moderate source of protein and fiber, contributing to satiety.
Moderation is key; enjoying it occasionally as part of a varied and nutritious diet is unlikely to cause significant harm. For example, incorporating a grilled cheese sandwich into a meal with a side salad and fruit can help balance the nutritional profile and provide a more complete and healthy meal.
Key Questions Answered
Can I make a grilled cheese vegan?
Absolutely! Swap the cheese for vegan cheese alternatives and use vegan butter or oil.
Is grilled cheese high in sodium?
It can be, depending on the type of cheese and bread used. Opt for lower-sodium options to keep it in check.
What kind of cheese is best for a low-fat grilled cheese?
Part-skim mozzarella or reduced-fat cheddar offer a lower-fat option without sacrificing too much flavor.
How many calories are in a typical grilled cheese?
That depends on the size and ingredients, but a typical sandwich can range from 200-400 calories.
Grilled cheese, a comfort food classic, boasts a surprisingly variable nutritional profile depending on the bread and cheese. Want a comparison to a fast-food favorite? Check out the quarter pounder with cheese nutrition facts to see how the calorie and fat content stacks up. Returning to our grilled cheese, remember that using whole-wheat bread and lower-fat cheese can significantly improve its nutritional value.