Boar’s Head Cheese Varieties and Ingredients: Boar’s Head Cheese Nutrition
Boar’s head cheese nutrition – Boar’s Head is a well-known brand offering a wide variety of cheeses, each with its unique blend of ingredients and flavor profiles. Understanding the ingredients in these cheeses is crucial for consumers making informed choices based on dietary needs and preferences. This section details the composition of several popular Boar’s Head cheeses, highlighting variations and comparing them to similar products from other brands.
Boar’s Head Cheese Variety and Ingredient Details, Boar’s head cheese nutrition
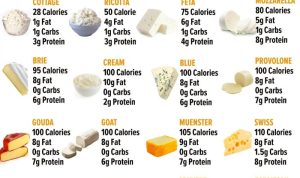
The following table provides a snapshot of several Boar’s Head cheese varieties, listing their primary ingredients, fat content, and sodium content. Note that these values can vary slightly depending on the specific batch and may not be perfectly consistent across all retailers. It’s always best to check the nutrition label on the specific package you purchase for the most accurate information.
The fat and sodium content are presented as approximations and may differ slightly depending on the specific product and packaging.
| Cheese Name | Primary Ingredients | Approximate Fat Content (%) | Approximate Sodium Content (mg per serving) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sharp Cheddar | Pasteurized Milk, Cheese Cultures, Salt, Enzymes | 33 | 220 |
| Colby | Pasteurized Milk, Cheese Cultures, Salt, Enzymes | 30 | 180 |
| Monterey Jack | Pasteurized Milk, Cheese Cultures, Salt, Enzymes | 28 | 160 |
| Provolone | Pasteurized Milk, Cheese Cultures, Salt, Enzymes | 32 | 200 |
| Pepper Jack | Pasteurized Milk, Cheese Cultures, Salt, Enzymes, Jalapeño Peppers | 30 | 240 |
Ingredient Variations Across Boar’s Head Cheese Types
The ingredient lists for Boar’s Head cheeses demonstrate a degree of consistency, with most varieties relying primarily on pasteurized milk, cheese cultures, salt, and enzymes. However, variations arise with the addition of flavorings, such as jalapeño peppers in Pepper Jack or herbs and spices in other specialty cheeses. Some cheeses might also include additional milkfat for a richer texture or different types of cheese cultures to achieve specific flavor profiles.
These subtle variations significantly impact the final taste and texture of the cheese.
Comparison to Other Brands
Comparing Boar’s Head cheese ingredients to similar cheeses from other brands often reveals similar core ingredients. Many brands use pasteurized milk, cheese cultures, salt, and enzymes as their base. However, differences can be found in the types of milk used (e.g., whole milk versus reduced-fat milk), the specific cheese cultures employed, and the presence of additives or preservatives. Some brands might use different types of salt or include additional ingredients for flavor enhancement or texture modification.
A direct comparison requires analyzing the specific ingredient lists of individual products from competing brands. This comparison can help consumers determine which brand best suits their dietary needs and preferences.
Micronutrient Content and Sources

Boar’s Head cheese, like many cheeses, offers a range of micronutrients vital for maintaining good health. These essential vitamins and minerals contribute to various bodily functions, and understanding their sources within the cheese can help consumers make informed choices about their diet. The specific micronutrient profile will vary slightly depending on the type of Boar’s Head cheese, as different cheeses utilize different milk types and aging processes.
The micronutrient content of cheese is largely determined by the milk it’s made from and any added ingredients during processing. Cow’s milk, the most common source for Boar’s Head cheeses, naturally contains several essential vitamins and minerals. Further processing and aging can influence the final concentration of these nutrients.
Key Micronutrients in Boar’s Head Cheese
Boar’s Head cheeses contain various micronutrients beneficial to health. The following list details key micronutrients and their likely sources within the cheese making process.
- Calcium: Primarily sourced from the milk used in cheese production. Calcium is crucial for strong bones and teeth, muscle function, and nerve transmission.
- Vitamin A (Retinol and Carotenoids): The amount of Vitamin A can vary depending on the type of cheese and the diet of the cows. Vitamin A supports vision, immune function, and cell growth.
- Riboflavin (Vitamin B2): Naturally present in milk, riboflavin contributes to energy metabolism and healthy skin.
- Vitamin B12: Found in milk, this vitamin is essential for nerve function, red blood cell formation, and DNA synthesis.
- Phosphorus: Another component of milk, phosphorus works alongside calcium for bone health and is involved in various metabolic processes.
- Zinc: Present in smaller amounts, zinc plays a crucial role in immune function, wound healing, and cell growth. The amount can vary based on the milk source and cheese aging process.
Micronutrient Role in Overall Health
The micronutrients found in Boar’s Head cheese contribute significantly to overall health and well-being. Adequate intake of these nutrients supports various bodily functions, preventing deficiencies that can lead to health problems.
Okay, so you’re tryna figure out the nutritional deets on Boar’s Head cheese, right? It’s def got some serious sodium, but also protein. Wanna compare it to something else? Check out the nutrition facts for bagel with cream cheese – it’s kinda wild how much fat’s in that. Anyway, back to Boar’s Head – it’s prob not the healthiest choice, but a lil slice won’t kill ya, lol.
For example, sufficient calcium and vitamin D intake are crucial for preventing osteoporosis, while adequate vitamin A and zinc support a robust immune system. Riboflavin and vitamin B12 are essential for energy production and nerve function. Phosphorus works with calcium for maintaining strong bones. A balanced diet including foods rich in these micronutrients helps to reduce the risk of various health issues and promotes overall well-being.
Comparison to Other Protein Sources
Compared to other protein sources, Boar’s Head cheese offers a unique micronutrient profile. While lean meats like chicken and fish provide excellent protein, they generally contain lower levels of calcium and certain B vitamins compared to cheese. Similarly, plant-based protein sources like beans and lentils are rich in some micronutrients but often lack vitamin B12, which is readily available in dairy products.
The nutritional value of Boar’s Head cheese makes it a valuable component of a balanced diet, particularly for individuals seeking a convenient source of protein and essential micronutrients.
Allergens and Dietary Restrictions

Choosing cheese can be a challenge for individuals with allergies or dietary restrictions. Boar’s Head offers a wide variety of cheeses, but understanding their ingredients is crucial for safe consumption. This section details potential allergens in Boar’s Head cheeses and provides guidance for making informed choices.
Several Boar’s Head cheese varieties contain common allergens. It’s vital to carefully check the ingredient list on each package before consuming any product, as formulations can vary.
Potential Allergens in Boar’s Head Cheese Products
The following allergens are frequently found in various Boar’s Head cheese products. Always refer to the product label for the most up-to-date and complete allergen information, as formulations may change.
- Milk: This is a primary ingredient in all cheeses and is a major allergen for many people.
- Soy: Some Boar’s Head cheeses may contain soy lecithin as an emulsifier.
- Eggs: While less common in cheese production, some specialized varieties might include egg products.
- Wheat: Some flavored cheeses may contain wheat-based ingredients.
- Tree Nuts: Certain flavored cheeses may contain nuts or nut oils as part of their flavor profile. Always check the label for specific nut declarations.
- Peanuts: While less frequent, some flavored varieties might contain peanut ingredients.
Choosing Boar’s Head Cheese for Dietary Restrictions
Individuals with lactose intolerance or gluten sensitivity can still enjoy Boar’s Head cheese, provided they select appropriate options. Careful label reading is paramount.
For lactose intolerance: While most Boar’s Head cheeses contain lactose, some varieties may offer reduced lactose content or be processed in ways that minimize lactose impact. Look for products labeled as “reduced lactose” or those with lower lactose percentages indicated on the nutritional information panel. Completely lactose-free options are not typically found in the Boar’s Head range.
For gluten sensitivity: The majority of Boar’s Head cheeses are naturally gluten-free. However, always check the label to ensure that no gluten-containing ingredients, such as flavorings or additives, have been added. Products explicitly labeled as “gluten-free” provide additional assurance.
Navigating Boar’s Head Cheese Product Labels
Understanding how to read Boar’s Head cheese labels is crucial for avoiding allergens. The following steps will help you navigate the label effectively:
- Ingredient List: Carefully review the complete ingredient list. Allergens are clearly listed in bold or italics, according to regulations.
- Allergen Statement: Look for a dedicated allergen statement, usually found near the ingredient list, that explicitly lists potential allergens present in the product.
- “May Contain” Statement: Pay close attention to “May Contain” statements, indicating the potential for cross-contamination during manufacturing.
- Contact Information: If you have questions or concerns, use the contact information provided on the packaging to reach Boar’s Head directly.
Key Questions Answered
Is Boar’s Head cheese suitable for a low-sodium diet?
Some Boar’s Head cheeses have lower sodium content than others. Check the nutrition label for specific sodium levels and choose accordingly.
Does Boar’s Head cheese contain gluten?
Most Boar’s Head cheeses are naturally gluten-free, but always check the label to ensure it’s suitable for those with gluten sensitivities.
What are the best Boar’s Head cheeses for a low-fat diet?
Look for varieties labeled as “light” or “reduced-fat” to minimize fat intake. Compare fat content per serving on the nutrition labels.
Can I find the nutritional information online?
Boar’s Head’s website and product packaging provide detailed nutritional information for their cheeses.